Comparative Analysis of Merge Trees using Local Tree Edit Distance
Raghavendra Sridharamurthy, Vijay Natarajan
View presentation:2022-10-21T14:24:00ZGMT-0600Change your timezone on the schedule page
2022-10-21T14:24:00Z
Prerecorded Talk
The live footage of the talk, including the Q&A, can be viewed on the session page, Comparisons.
Fast forward
Keywords
Merge tree, scalar field, local distance measure, persistence, edit distance, symmetry detection, feature tracking.
Abstract
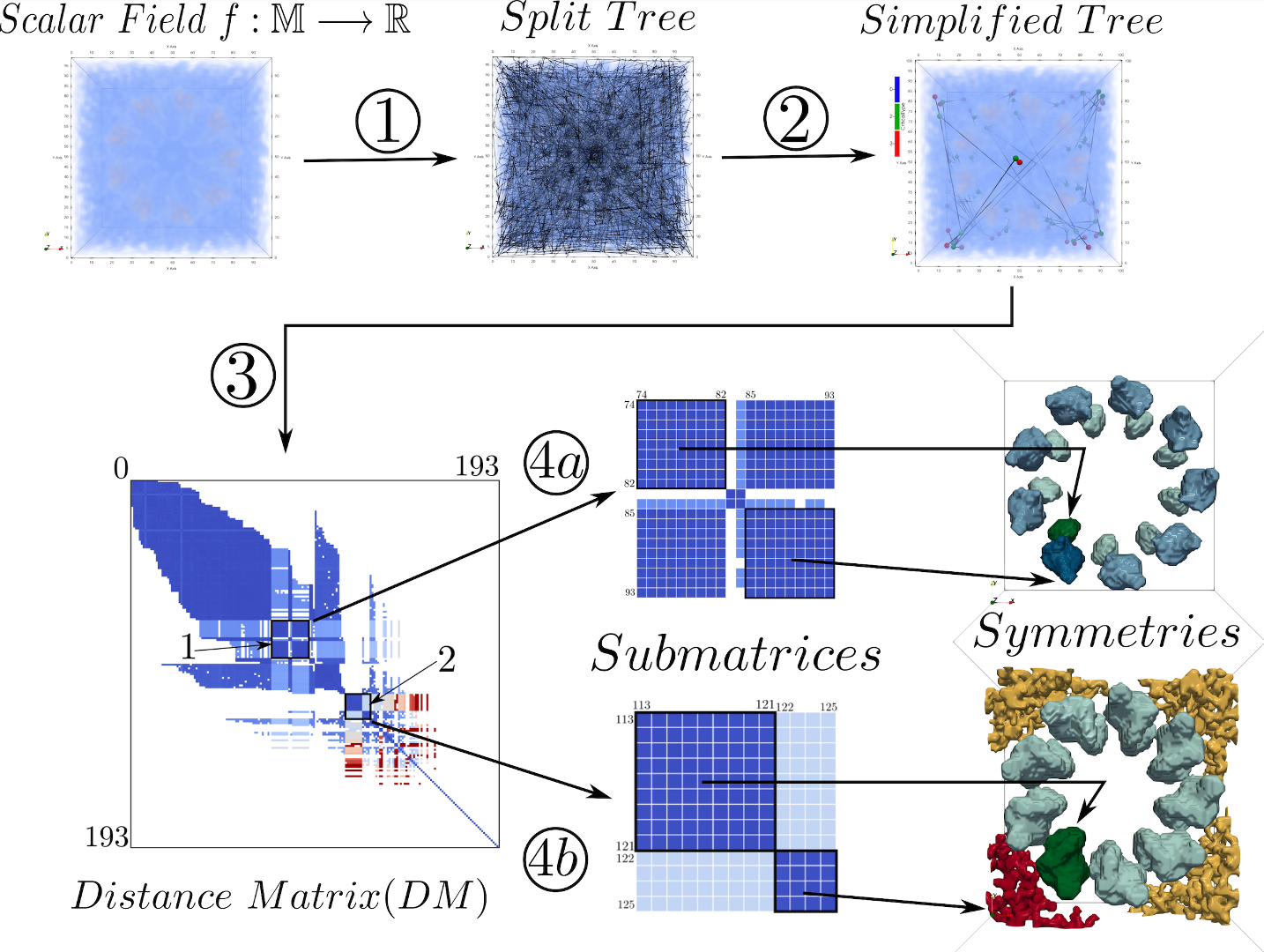
Comparative analysis of scalar fields is an important problem with various applications including feature-directed visualization and feature tracking in time-varying data. Comparing topological structures that are abstract and succinct representations of the scalar fields lead to faster and meaningful comparison. While there are many distance or similarity measures to compare topological structures in a global context, there are no known measures for comparing topological structures locally. While the global measures have many applications, they do not directly lend themselves to fine-grained analysis across multiple scales. We define a local variant of the tree edit distance and apply it towards local comparative analysis of merge trees with support for finer analysis. We also present experimental results on time-varying scalar fields, 3D cryo-electron microscopy data, and other synthetic data sets to show the utility of this approach in applications like symmetry detection and feature tracking.